Triangle Area Guide: Formulas and Methods for Finding the Area of Triangles
Comprehensive Definition, Description, Examples & Rules
Introduction to Triangle Area
Calculating the area of a triangle is crucial for determining the amount of space it occupies. Triangles are fundamental geometric shapes, and they can be subdivided into smaller, perfect triangles to calculate the overall area. This understanding allows for accurate measurements and proper space allocation when working with irregular shapes like polygons.
There are different methods by which you can calculate the area of a triangle, and it is essential to understand all the methods as it is different for each type of triangle. There are different formulas to calculate the area of different triangles. The formula depends upon the type and the degree of the triangle you are calculating.
Basic Concepts
Area of Triangle Formula
The standard formula that you can use to calculate the area of a triangle is:
- ½ × base × height
You use this formula for all standard triangles with a base and a height.
Examples
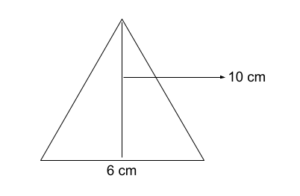
Calculating the area:
½ * 6 * 10 = 30 cm2
It is a simple example; you can use this technique and formula to calculate the triangles’ area.
How to Find the Area of a Triangle
The step-by-step guide you need to follow for calculating the area of a triangle with the basic formula is:
- Identify the type of triangle you are calculating.
- Check and identify the angles of the triangle.
- Calculate the height of the triangle if not given.
- Use the formula ½ × base × height and get your result
Diagrams
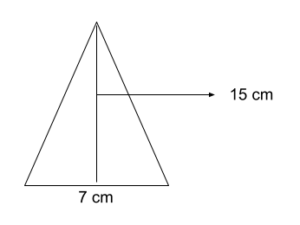
Calculating the area:
½ * 7 * 15 = 52.5 cm2
This diagram is an example that can greatly enhance your understanding of the concepts through its comprehensive area calculation.
Right-Angled Triangle Area
For calculating the right angled triangle area, you can use the basic standard formula for finding the area of triangle with angle that is ½ × base × height.
To calculate the area of a right-angle triangle, you can also use the Pythagorean theorem. Formula:
(hypotenuse)² = (base)² + (altitude)²
You can use any of the two formulas to calculate a right-angle triangle’s area.
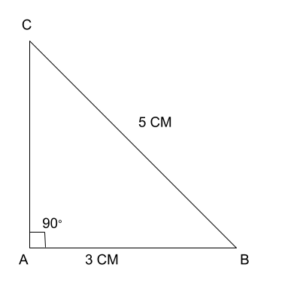
Practical examples
BC = Hypotenuse
Required side = AC (Height)
Therefore, BC2 = AC2 + AB2
52 = AC2 + 32
AC2 = 25 – 9
AC2 = 16
AC2 = 42
AC = 4 CM
So, height is 4 C
Area: ½ * 3 * 4 = 6 CM2
An example of how to calculate the area of a triangle using the standard formula is given above. This example is how to calculate the side by using the Pythagoras theorem.
Advanced Methods
Area of a Triangle Sine Rule
The sine rule states the ratio between the length of a side of a triangle to the sine of its angle at the opposite side. It happens for all the sides and angles of a particular triangle while calculating its area. You calculate using this rule when it is not a right-angled triangle.
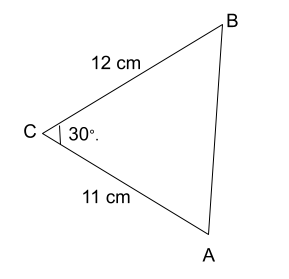
Examples
Formula for area = ½ * ( side * side ) * Sin Angle
½ * (11 * 12) * Sin 30
½ * 132 * 0.5
66 * 0.5
So, the area is 33 Cm2.
It is an example of how you can apply the sine rule and calculate the area of a triangle that is not at a right angle.
Surface Area of a Triangle
The surface area of a triangle is the amount of space the triangle covers outside. The surface area of the triangle is similar to the standard area of the triangle, and it similarly applies to the triangle. The formula to calculate the surface area of a triangle is different according to Heron’s formula. It is:
√{ S (S – a)(S – b)(S – c) }
The step-by-step guide on how to find the surface area of a triangle includes:
- Identify the type of the triangle, calculate the sides, and name them ‘a’, ‘b’, and ‘c’.
- Calculate the semi-perimeter of that triangle using the formula:
(a + b + c)/ 2 and denote it as ‘S’.
- Use the heron’s formula mentioned above to calculate the total surface area of the triangle.
Triangle Area and Trigonometry
Trigonometry is the study you perform to identify the relationship between the angles and the side length in a triangle. You calculate the economic ratios of a triangle, and it helps to calculate the exact area of the triangle. The formula for the area of a triangle trigonometry using the trigonometric formula will be
½ × b × c × sin(a)
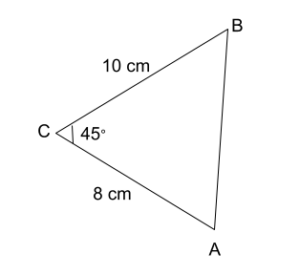
Examples
Formula for area = ½ * ( side * side ) * Sin Angle
½ * (10 * 8) * Sin 45
½ * 80 * 0.707
40 * 0.707
So, the area is 28.28 Cm2. (Approx)
It is an example of how you use a trigonometric formula to calculate the area of a triangle.
Area of a Triangle with Angle
To calculate the area of a triangle when one or more angles are given, you can use that trigonometric formula for each of the given angles. The basic trigonometric formula mentioned above is the primary formula that you can use for calculating the area of a triangle with angle. If more than one angle of the triangle is given, you can use the formula:
a / Sin A = b / Sin B = c / Sin C
It is a difficult formula for you to use when mentioning two angles between the two sides of the triangle.
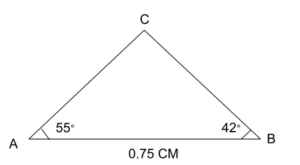
Example
A = 45°
B = 60°
C = 180° – 55° – 42°
= 83°
0.75/Sin 83 = a/ Sin 55 and 0.75/Sin 83 = b/Sin 42°
a = 0.75 Sin 55/Sin 83 and b = 0.75 Sin 42/Sin 83
a = 0.62 CM
B = 0.51 CM
Area = ½ * ( side * side ) * Sin Angle
½ * (0.62 * 0.51) * Sin 83
Area = 0.153 CM2 (Approx)
It is an example of how you can use the angle of a triangle to calculate its area effectively when more than one angle is given.
Real World Applications
You can use the area of a triangle in all your real-life scenarios, and the examples are:
- Engineers calculate the triangle’s area during construction by using a right-angle triangle shape to calculate the measurements and make their calculations in areas of the triangle.
- Building any new architecture involves the calculation of the area of the triangle and has an important role in building architecture with proper measurements.
- Art and design also have the importance of the shape of the triangle, and how the area is calculated is also very important.
Challenges and Problem-solving
Trigonometric formulas and other complex mathematical equations can be challenging to work with. Calculating the area of a triangle or surface becomes more difficult when using these types of formulas.
To calculate the area of a triangle, you first need to determine the lengths of its sides and angles. Understanding the formula and how to apply it is key to solving math problems. To solidify your comprehension, you can take the practice exercise mentioned below.
Step Up Your Math Game Today!
Free sign-up for a personalised dashboard, learning tools, and unlimited possibilities!

Key Takeaways
- The formula for calculating the area of the triangle is different for all types of triangles.
- You will use the standard formula when you know the base and height of the triangle.
- The Pythagoras theorem is for the right angle triangle, i.e., 90°
- It is difficult to calculate trigonometric formulas and can be challenging at times, but you need to follow the rules and understand the type of triangle to calculate its area.
- You can use the area of the triangle daily as it involves practical human life calculations.
Quiz
Question comes here
Frequently Asked Questions
A scalene triangle is a type of triangle in which all three sides of the triangle have different lengths, and all three angles also have a different measure. The total sum of all the interior angles of the triangle always comes to 180°. To calculate the area of a scalene triangle, you use the standard formula:
- ½ × base × height.
When calculating the area of a triangle, the base and height are crucial factors. The standard formula for finding the area involves determining these measurements. The base refers to the side that serves as the foundation for the triangle, while the height is measured from the midpoint of the base to where it intersects with the other two sides.
Trigonometry plays a crucial role in calculating the area of a triangle, especially when you have information about the angles involved. Using the triangle’s given angles, you can employ trigonometric formulas to determine the area. Formula:
½ × b × c × sin(a)
Here, ‘b’ and ‘c’ are sides of the triangle, while ‘a’ is the angle of the triangle.
If more than one side is given, then you will use the trigonometric formula:
a / Sin A = b / Sin B = c / Sin C
To calculate a side
You can use both these trigonometric formulas to calculate the exact area of the triangle.
One important distinction between the perimeter and area of a triangle is their respective definitions. The area refers to the actual region occupied by the triangle, while the perimeter represents the total length of its outer boundary. Together, these measurements provide key information regarding the size and dimensions of the triangle.
There are many real-life applications where it is important to calculate the area of a triangle, and you have to use the formula of a triangle itself. These include:
- Measuring pyramids
- Carpenters use right-angle triangles for measurement.
- Tunnels and bridges