Exploring 2D Shapes: Definition, Examples, and Properties
Comprehensive Definition, Description, Examples & Rules
Introduction
2D shapes are shapes that have two dimensions which are height and width. These shapes have different features according to the different types. A 2D shape is important to see and describe the shape around you. It can help you with mathematics and problem-solving.
Comparison
2D shapes definition is one that has only a length and width. These are:
- width
- height.
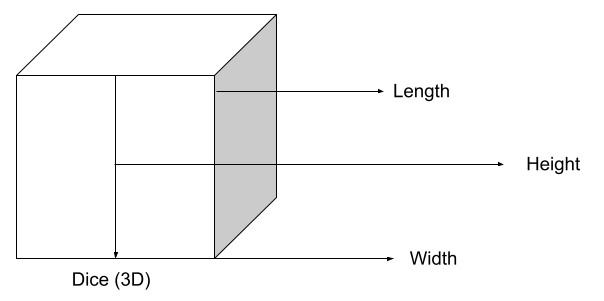
On the other hand, 3D shapes are different figures. These include:
- Length
- Width
- Height.
The 2D shape is flat, while the 3D shape has a different size and perspective.
Importance
You need to understand the importance of 2D shapes according to different contexts. These are:
- Help the students to write numbers and read quickly.
- You can understand more complex concepts of maths by using two-dimensional shapes.
- It Helps you to learn more art skills and has an impact on drawing and painting lessons.
- You get a visual understanding of the shapes. It becomes easy to find different symbols and signs. It will help you to develop awareness about objects.
- You will understand a lot about geometrical attributes if you read the properties of 2D shapes.
Names and Examples of 2D Shapes
The names of 2D shapes are famous and you can use them in your day-to-day life. The famous 2D shapes names are:
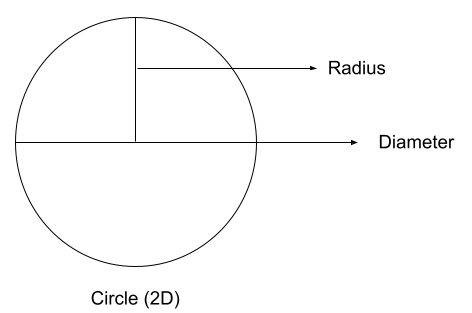
Circle: A circle is a familiar and widespread shape. It is without corners or angles and has a unique roundness. It has an unchanging radius and diameter.
Square: A square is a shape having four equal sides. In addition, the length and width of a square are always equal.
Rectangle: A rectangle is a geometric shape characterized by two sides of equal length. These sides contribute to the symmetrical nature of the shape, making it balanced.
Triangle: A triangle always consists of three sides. These sides can have either two or three equal lengths, depending on the situation.
Pentagon: A Pentagon is a 2D shape that consists of five straight sides, and all the signs of the Pentagon can be equal or unequal depending upon the situation.
Hexagon: A hexagon is a 2D shape that consists of 6 sides, and the sides can have equal lengths and unequal lengths.
You can identify these shape names with sides according to the characteristics. There are many names of shapes 2D.
Examples of real-life objects which are 2D shapes:
The 2D Shapes examples are:
- Clock – Circle or Square
- Window – Square or Rectangle
- Plate – Circle
- Television – Rectangle
Understanding the Properties of 2D Shapes
There are important properties of 2D shapes that you effectively have to understand. These are:
- Sides: One key feature of 2D shapes is their ability to have varying sizes. Additionally, each shape possesses sides with different lengths and widths.
- Angles: All 2D shapes have different angles, like triangles or rectangles. All of these form different angles, which is an important property.
- Symmetry: All 2D shapes have different symmetry, and all these shapes have different types.
The difference is that regular shapes have angles on sides of equal value and the same length. The other has variable sides and different values for the angles.
The properties of the different types of 2D shapes are:
- Circle: The property of a circle is that it consists of a constant radius and diameter.
- Square: The property of a square is that it consists of all equal sides with equal lengths.
- Rectangle: The property of a rectangle is it consists of two equal sides that correspond to each other.

Difference Between 2D and 3D Shapes
The 2D shapes and 3D shapes are the main part of the shapes, and there is a major difference between 2D and 3D shapes. These are:
- A 2D shape is a two-dimensional figure that exists on a flat surface, while a 3D shape is a three-dimensional object that occupies space.
- A 2D shape consists of only width and height, while a 3D shape consists of length, width, and height.
The 2D and 3D shapes have different sizes and depths according to many shapes.
Visual Representation
This is a 2D shape.
This is a 3D shape.
Practical Applications of 2D Shapes
You can apply 2D shapes in many fields and use them in regular representation. The 2D Shapes in regular life are:
- Architecture: Circles, Triangle, and Squares help to design a particular building.
- Design: Hexagon, Octagon that can help to design a place.
2D shapes have a great role in art and engineering, and both have a good role in it. If you want to understand, you must understand the different two-dimensional shapes.
Engineering has a lot to do with shapes. If you have to understand engineering, you must understand the shapes. For that, you need to use it in the engineering process. Different shapes have different representations that you need to understand.
The two-dimensional shapes have a big contribution to the visualization that you can have. Visualizing the different shapes will be very helpful if you understand the different visualization types. There have been many theories in which there will be an effective contribution of the shapes for solving mathematical problems.
Step Up Your Math Game Today!
Free sign-up for a personalised dashboard, learning tools, and unlimited possibilities!

Key Takeaways
- 2D shapes have two elements and are flat shapes.
- These shapes help in problem-solving and in visualization.
- All 2D shapes have different properties, which you must understand according to the shape you see.
- You can identify the different types of these shapes in many ways.
Quiz
Question comes here
Frequently Asked Questions
A polygon is a 2D Shape with at least three straight sides. Some examples of 2D shapes include triangles, quadrilaterals, and squares.
Shapes can be identified by their unique properties. Each shape possesses distinct characteristics that can help determine its name. Additionally, shapes have many other properties and hold different meanings.
The properties of 2D shapes are for the different types of shapes. These are:
- Circle: The property of a circle is that it has a constant radius and diameter.
- Rectangle: The property of a rectangle is that it consists of two equal sides for corresponding sides.
- Square: The property of a square is that it consists of four equal sides.
You can calculate it according to the different types of shapes. These are:
- Square: Side × 2
- Rectangle: Length and Width
- Triangle: 1/2×Width×Height
A two-dimensional shape can be symmetrical when you draw a line through it, and either side of the reflection will fall on the other side. The line drawn in between is the line of symmetry.
The real-life examples of two-dimensional shapes that you can see are:
- Circle: Volleyball
- Square: Photo Frame
- Rectangle: Box