Learn English
Future Continuous Tense
Phonetics:
fjuːtʃə(r)
kənˈtɪnjuəs
tens
Pronunciation:
Embrace the Flow: Understanding the Future Continuous Tense in Action
Comprehensive Definition, Description, Examples & Rules
Introduction to the Future Continuous Tense:
The future continuous tense is employed to articulate actions that will be in a state of progress at a designated moment in the future. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will” followed by the verb “be” and the present participle form of the main verb. For example, “I will be studying” or “They will be playing.” This tense is often used to talk about future plans or actions that will be happening over a period of time.
This subject is widely used in different fields and has a structured approach to learning. It covers key concepts, theories, and principles in a progressive manner. With clear explanations, examples, and visual aids, students can understand and apply the subject effectively. Practice exercises and review questions further reinforce learning. Mastering this subject provides a strong foundation for future academic or professional endeavours.
Formation and Usage of the Future Continuous Tense:
The future continuous tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will” followed by “be” and the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb. It is employed to delineate actions or events that will be underway at a designated point in the future. For example, “I will be studying tomorrow evening.” Here, “will” the shows future tense, “be” indicates the continuous aspect, and “studying” is the present participle of the main verb “study.” The future continuous tense helps us talk about ongoing actions that will happen at a later time.
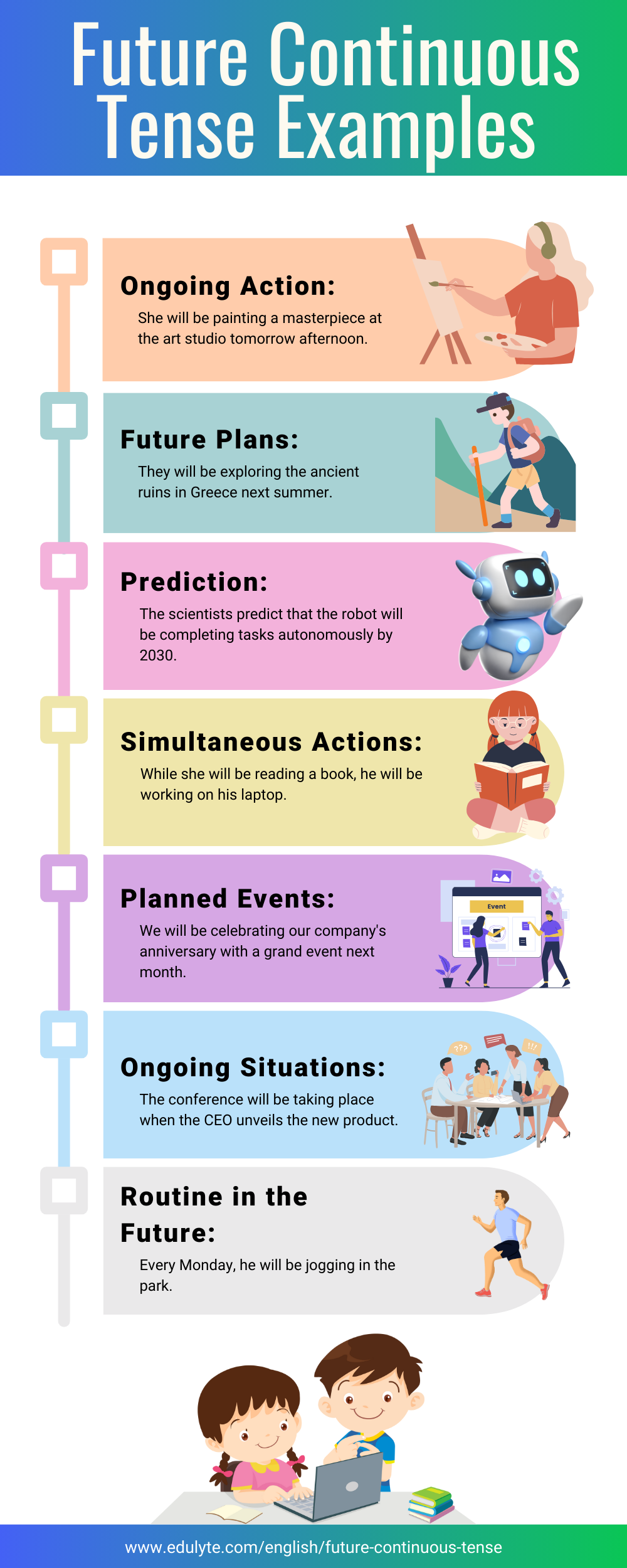
- Sarah will be travelling to Paris next week.
- We will be watching a movie tonight.
- They will be studying for their exams tomorrow.
- He will be cooking dinner while I clean the house.
- The team will be practising for the big game all day.
- I will be working on my project during the weekend.
- Application of the Future Continuous Tense:
The future continuous tense is a syntactic structure employed to articulate actions or events that will be in a state of progress at a designated juncture in the forthcoming period. It is commonly employed to express future plans, ongoing actions, or predictions. For example, we use it to discuss activities happening at a specific time in the future, such as “Tomorrow, I will be studying for my exams,” or to discuss ongoing situations that will continue in the future, like “They will be travelling to Europe next month.” By using the future continuous tense, we can convey a sense of continuity and anticipate events that will be unfolding in the days to come.
Present progressive tense is used to describe ongoing actions or future plans. When we want to talk about something that is happening right now or in the near future, we use this tense. The future continuous tense is constructed by the combination of the present tense forms of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) with the present participle of the main verb. For example, “I am studying” shows an ongoing action, while “We are going to the park tomorrow” indicates a future plan. By using the present progressive tense, we can express actions that are happening at the moment or scheduled to take place in the future.
Passive Voice in the Future Continuous Tense
The passive voice is a grammatical structure utilized in English to place emphasis on the recipient of an action, rather than the agent performing the action. In active voice constructions, the subject acts as the agent of the action, whereas in passive voice constructions, the subject assumes the role of the recipient of the action. Understanding and correctly using passive voice future continuous tense is important in English grammar as it allows for variation in sentence structure, provides a different perspective, and highlights the object or recipient of the action. To learn more about passive voice and its usage, you can refer to the Passive Voice page.
In the future continuous tense, the passive voice is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will be” followed by the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb and the word “being.” This structure emphasizes an ongoing action that will be performed by the subject in the future. For example, instead of saying “The teacher will be grading the exams,” in the active voice, we can say “The exams will be being graded by the teacher,” in the passive voice, where “will be” is the auxiliary verb, “being” is added after the present participle “grading,” and the subject “the teacher” becomes the object of the sentence.
The passive voice in the future progressive tense is used when the subject of the sentence is receiving the action in a continuous form in the future. For example, “The cake will be being baked by the chef tomorrow.” In this sentence, the subject “cake” is being acted upon (“being baked”) by the chef in the future (“tomorrow”). The passive voice future continuous tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will be” followed by the present participle of the main verb (“being baked”). It is important to note that the passive voice emphasizes the action being done to the subject rather than the doer of the action.
Active Voice vs. Passive Voice in the Future Continuous Tense:
Active voice and passive voice in the future continuous tense have distinct ways of expressing actions. In active voice, the subject of the sentence performs the action, while in passive future continuous tense, the subject receives the action. For example, in active voice, “She will be painting the house” highlights the subject (she) actively engaging in painting, while in passive voice, “The house will be painted by her” emphasizes the object (the house) being acted upon. Active voice focuses on the “doer” of the action, while passive voice emphasizes the “receiver” of the action.
In writing, the choice of active or passive voice depends on the emphasis and focus of the sentence. Active voice is used when the subject performs the action, which adds clarity and directness to the sentence. It is suitable for highlighting the doer of the action and creating an engaging tone. On the other hand, passive future continuous tense is employed when the subject receives the action, placing emphasis on the action itself or the object of the action. It can be used to downplay the doer or to maintain a more formal tone.
Transform Your English Skills
Free sign-up for a personalised dashboard, learning tools, and unlimited possibilities!
Sign up Now
Key Takeaways
- The future progressive tense is formed using the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall” + “be” + the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
- It is used to describe ongoing actions that will happen at a specific time in the future.
- The future continuous tense emphasizes the continuity and duration of the action.
- The negative form of the future continuous tense is formed by adding “not” after the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall.”
- The future continuous tense is different from the future perfect tense, which describes actions that will be completed before a specified time in the future.
- Understanding when to use the future continuous tense can enhance your writing and add more depth to your descriptions.
- Practising exercises and activities, such as sentence construction and question formation, can help solidify your understanding of the future continuous tense.
- Online resources and worksheets, such as those provided by Edulyte, can offer additional practice and guidance for mastering the future continuous tense.
- Embracing the flow of the future continuous tense will allow you to express ongoing actions with clarity and precision, making your writing more engaging and dynamic.
Quiz
Question comes here
Frequently Asked Questions
To make a negative sentence in the future continuous tense, you use the auxiliary verb “will” (or “shall”) + “not” + be + the present participle of the main verb (-ing form). For example, “I will not be studying tomorrow.”
The auxiliary verbs used in the future progressive tense are “will” and “be.” “Will” is used to indicate future tense, while “be” is the auxiliary verb that is conjugated according to the subject and is followed by the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
The future continuous tense and the future perfect tense have distinct differences. The future progressive tense is used to describe an ongoing action that will happen at a specific time in the future. For example, “They will be travelling to Paris next week.” On the other hand, the future perfect tense is used to describe an action that will be completed before a specified time in the future. For example, “By the time she arrives, we will have finished our dinner.”
To improve your understanding of the future progressive tense, you can engage in various exercises and activities. Edulyte’s worksheet, which can be found below on this web page, could be a valuable resource. Additionally, you can find numerous online resources such as grammar websites, English learning platforms, and educational YouTube channels that offer exercises and explanations on the future continuous tense. Practice writing your own sentences and asking and answering questions using this tense to reinforce your understanding.


