Want to stand out in the accountancy and finance world? CPA Australia gives you the...
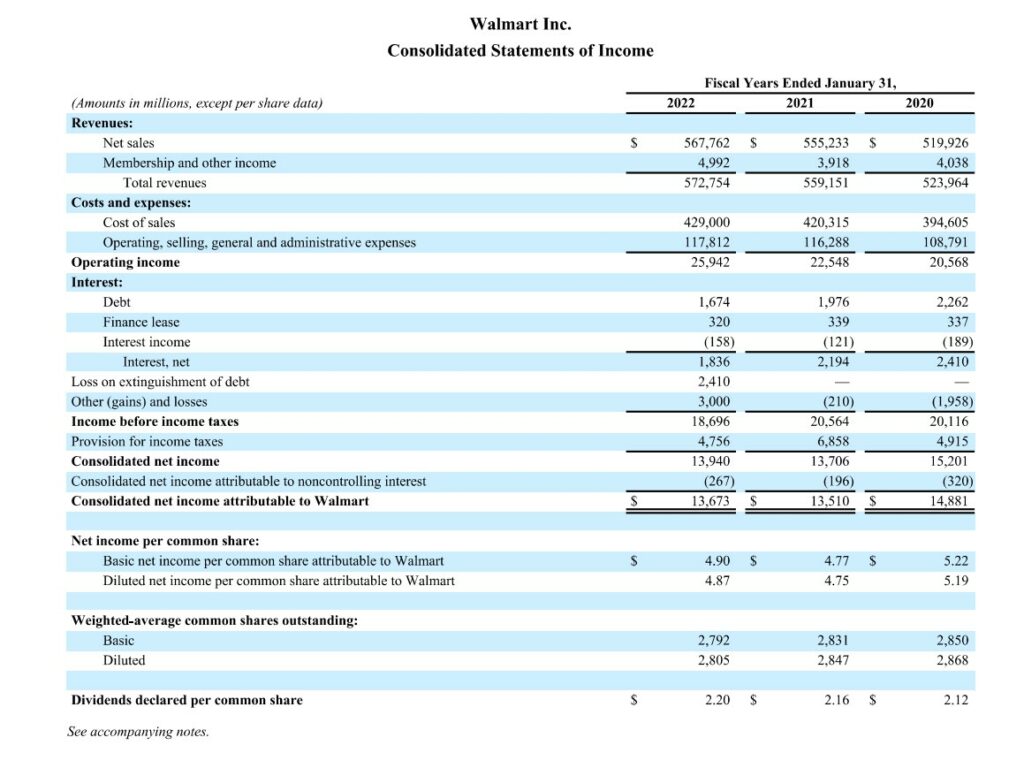
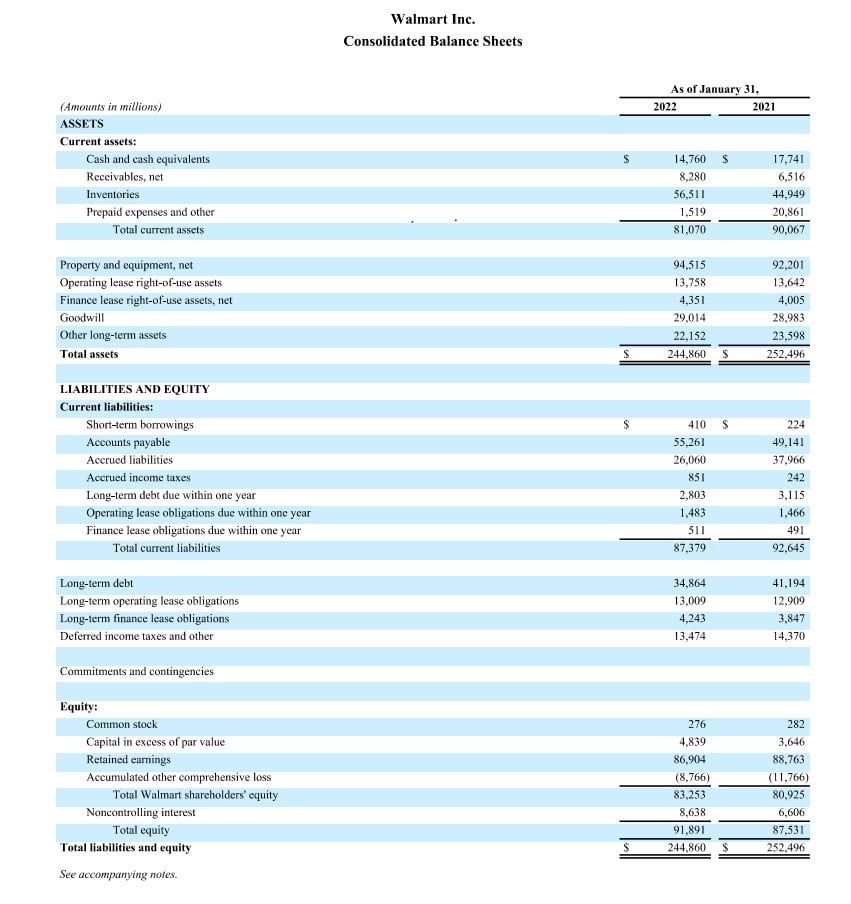
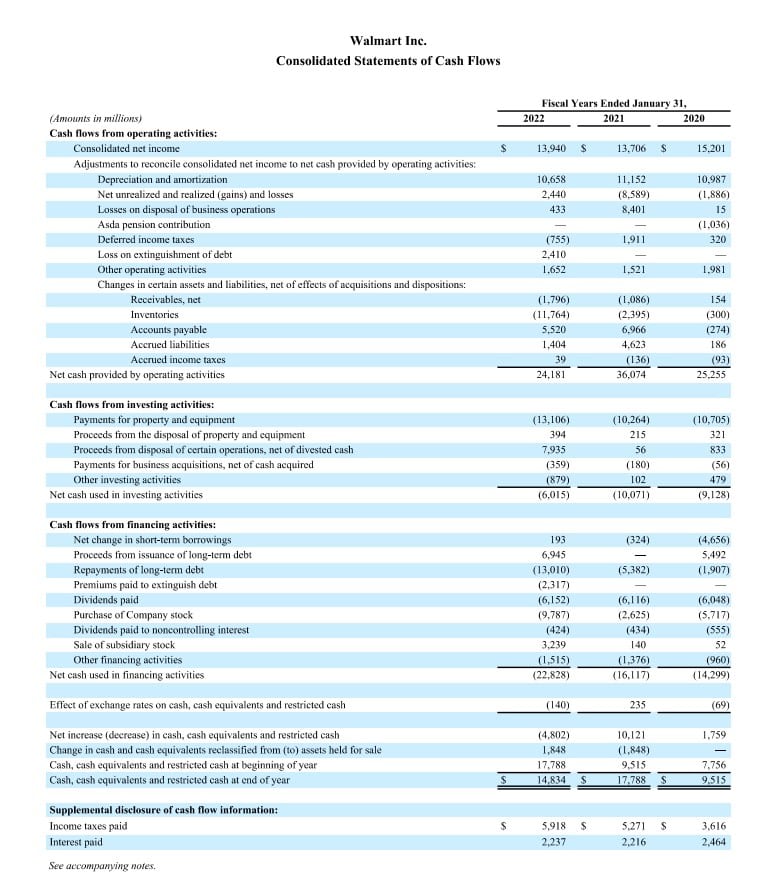
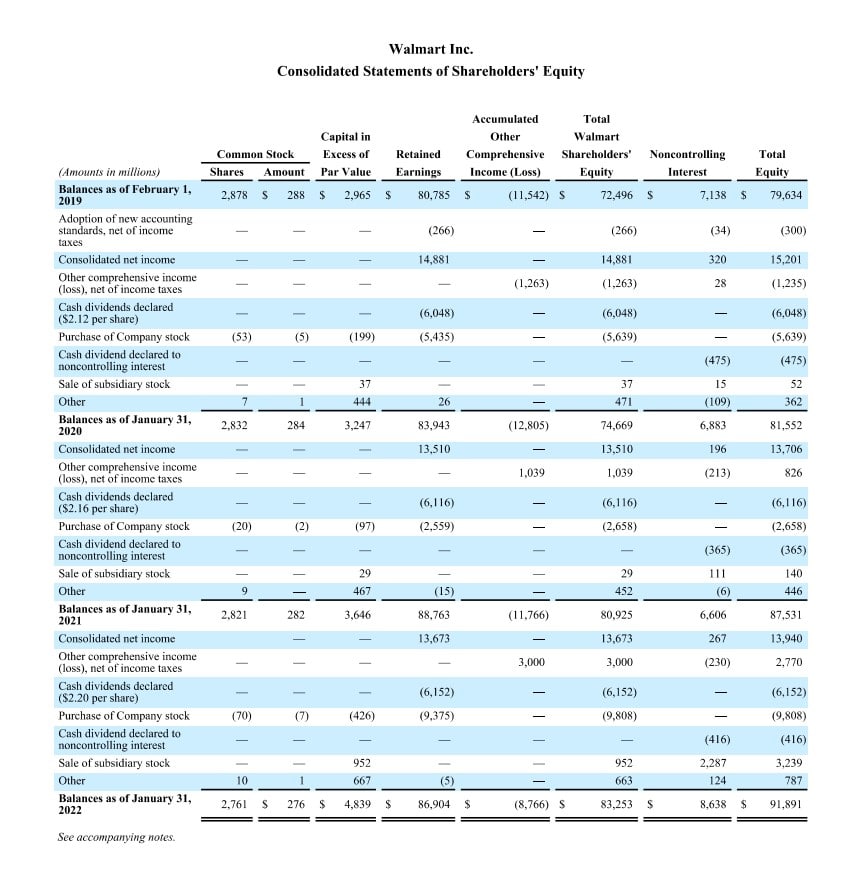
Read MoreAccounting is an essential part of running a business. It involves recording, classifying, summarising, and analysing financial transactions to help enterprises to make informed decisions. Accounting also allows companies to comply with tax laws and regulatory requirements. Therefore, a firm grasp of accounting basics and principles is crucial for every budding entrepreneur or anyone aiming to work in finance. With this knowledge, business owners and financial professionals can make sound financial decisions and ensure the financial health of their organisations.
Accounting Basics
Your Ultimate Guide | Understand the Language of Business | Accounting 101
Become fluent in accounting basics and its variables with insights from our accounting experts.
Written by: Edulyte Expert